Age Estimated Within 1.36 Years Using DNA Methylation Patterns
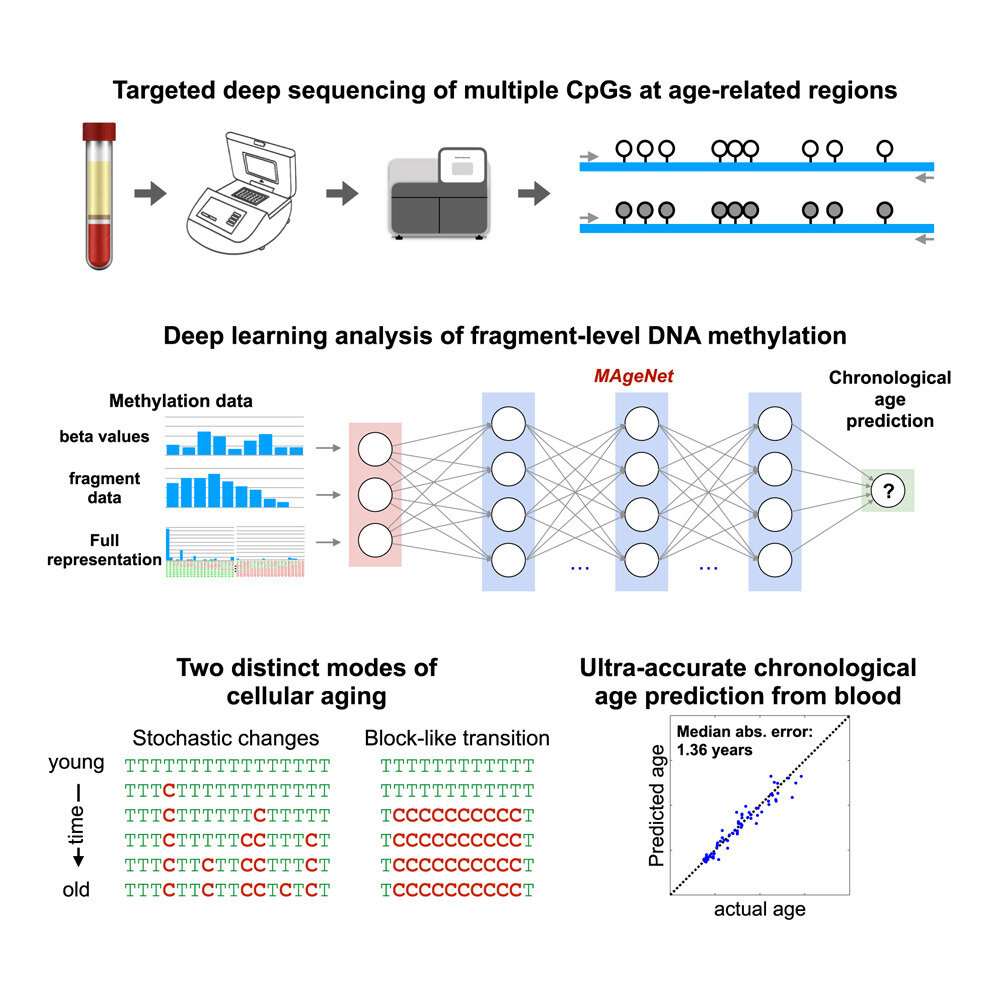
Scientists from the Hebrew University have created a highly precise technique for estimating biological age through DNA analysis, relying on just two small sections of the genome. By employing deep learning models that examine DNA methylation patterns at the level of individual molecules, they attain age estimates with a median error as minimal as 1.36 years among people younger than 50. This approach remains independent of factors such as smoking habits, body mass index, and gender, offering possible uses in forensic science, studies related to aging, and tailored medical treatments.
Subscribe to our newsletter for the most recent science and technology news.
A group of scientists from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, including Bracha Ochana and Daniel Nudelman, with guidance from Prof. Tommy Kaplan, Prof. Yuval Dor, and Prof. Ruth Shemer, have created an exceptionally accurate technique to determine someone's age using only a tiny DNA sample—showing significant promise for medical applications, studies on aging, and criminal forensics.
Leveraging advanced artificial intelligence, researchers developed a system known as MAgeNet capable of estimating an individual's actual age—how many years they have lived—with an accuracy within just 1.36 years for those younger than 50. The process only requires a basic blood sample.
Interestingly, the passage of time imprints detectable changes on our DNA," stated Professor Kaplan. "Our model interprets these signs with remarkable accuracy.
The key is found in how our DNA evolves over time via a mechanism known as methylation—chemically marking DNA with methyl groups (CH). 3 ) By focusing on two specific areas of the human genome, the researchers were able to detect these modifications at the molecular level, then apply deep learning techniques to convert them into precise age estimates.
The study, published in Cell Reports, Examined blood specimens from more than 300 individuals with good health, along with information gathered from a ten-year long-term study known as the Jerusalem Perinatal Study (JPS), directed by Professor Hagit Hochner from the School of Medicine. According to their findings, the model performed reliably under various factors—including cigarette use, physical mass, gender, and multiple indicators of cellular aging.
In addition to possible medical applications, this technique might transform forensic science by enabling specialists to determine a person's age based solely on a small sample of DNA—an area where current methods face difficulties.
This offers a fresh perspective on the mechanisms of aging at the cellular level," stated Professor Dor. "It's an impressive illustration of where biology intersects with artificial intelligence.
The study also revealed novel trends in how DNA evolves with time, indicating that our cells record aging through random processes as well as synchronized waves—similar to ticking internal biological timers. "It's more than simply determining your age," noted Dr. Shemer. "It's about grasping how your cells monitor time, one molecule at a time."
Significance: This study has the potential to change the way we handle health, aging, and personal identity moving forward. By enabling medical professionals to customize therapies according to an individual’s actual biological time line, as well as offering criminal investigators a valuable new method for crime resolution, the capacity to determine age through DNA paves the way for advancements throughout various fields such as science, healthcare, and legal systems. Additionally, this discovery enhances our comprehension of the aging process—moving us nearer to unraveling the body's inner timer.
More information: The passage of time is reflected through methylation alterations at specific clusters of CpG sites, Cell Reports (2025). DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115958 . www.cell.com/cell-reports/full … 2211-1247(25)00729-6
Supplied by the Hebrew University of Jerusalem
This narrative first appeared on Medical Xpress .
Posting Komentar untuk "Age Estimated Within 1.36 Years Using DNA Methylation Patterns"
Please Leave a wise comment, Thank you